Table of Contents
Overview
Have you ever been tripped up by a simple typo? We’ve all been there. You write color = "Red", but somewhere else, your code checks for "red", and your program breaks. It’s an all-too-common bug when dealing with user input, API data, or configuration files.
The Python enum module is a fantastic tool for managing a fixed set of constants, but by default, it’s case-sensitive. This can cause frustrating errors if you aren’t careful. But what if there was a better way? What if your enum could handle "RED", "red", and "Red" all gracefully?
The solution is quite simple. Let’s do it.
How to create case insensitive enum
First, let’s create one enum class to handle the missing values:
class CaseInsensitiveEnum(Enum):
@classmethod
def _missing_(cls, value):
# Convert the input value to lowercase for case-insensitive matching
value = str(value).lower()
for member in cls:
if member.value.lower() == value:
return member
# If no match is found, raise a ValueError
raise ValueError(f"'{value}' is not a valid {cls.__name__}")
# --- 1. FastAPI App and Input Validation ---And now you can create other enums that extend this enum to get the case-insensitive effect:
class ScriptLength(CaseInsensitiveEnum):
short = "short" # ~50-75 words
medium = "medium" # ~100-150 words
long = "long" # ~200-250 words
Now you can safely parse the enum no matter the case:
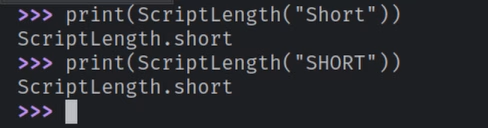
Obviously, you can get creative and create a catch-all for string value that cannot converge into a value after case conversion.

I build softwares that solve problems. I also love writing/documenting things I learn/want to learn.
