Table of Contents
Overview
If you are working on swing desktop app, MigLayout is a great library to help you layout your app quickly.
MiGLayout revolves around flexibility and simplicity while offering powerful features for fine-grained layout control. Here are the main concepts to understand when working with MiGLayout.
1. Components and Cells
- Each component in MiGLayout is placed into a cell within a grid.
- The grid dynamically adjusts based on the layout constraints, column/row constraints, and the components inside it.
- Components can span multiple cells, be aligned, resized, or stretched to fit the space.
2. Layout Constraints
- Purpose: Define global rules for the entire layout.
- Examples of global behaviors include:
- Wrapping components after a certain number (
wrap). - Adding padding around the layout (
insets). - Changing the flow of components (horizontal/vertical).
- Wrapping components after a certain number (
- Syntax is provided in the first argument of
new MigLayout().
Here are some examples
Wrap after x columns
class WrapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Wrap Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("wrap 3")); // Wrap after 3 components
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
panel.add(new JButton("Button " + i));
}
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
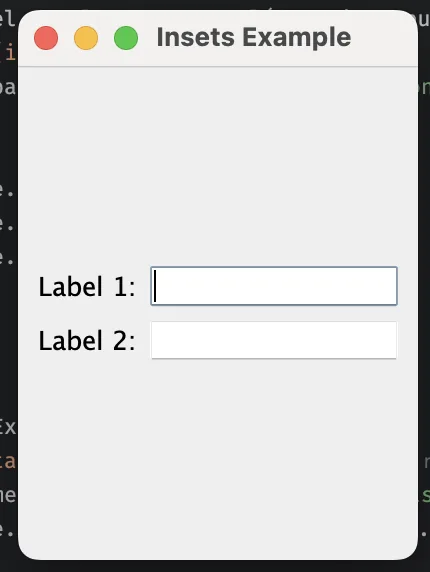
Padding with insets
class InsetsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Insets Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Add 10px padding on all sides
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("wrap 2, insets 100 10 100 10"));
panel.add(new JLabel("Label 1:"));
panel.add(new JTextField(10));
panel.add(new JLabel("Label 2:"));
panel.add(new JTextField(10));
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
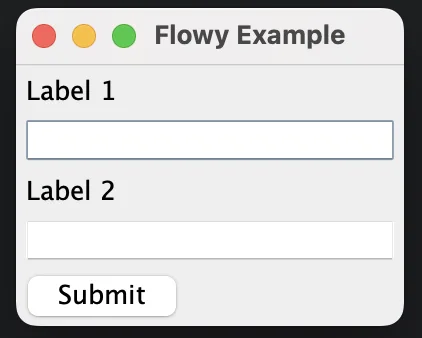
Changing the Flow of Components
class FlowyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Flowy Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Change flow direction to vertical
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("flowy, insets 5"));
panel.add(new JLabel("Label 1"));
panel.add(new JTextField(15));
panel.add(new JLabel("Label 2"));
panel.add(new JTextField(15));
panel.add(new JButton("Submit"));
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
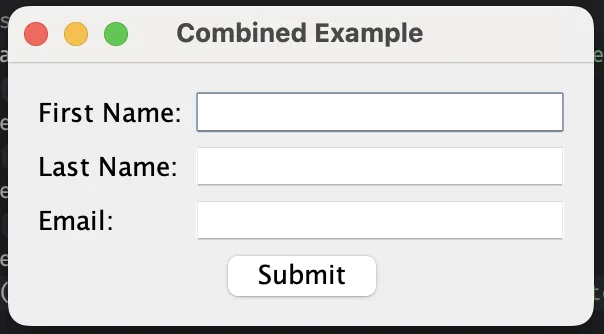
Combined example
class CombinedExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Combined Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Combine constraints: wrap, insets, and fill
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("wrap 2, insets 15, fillx"));
panel.add(new JLabel("First Name:"));
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "growx");
panel.add(new JLabel("Last Name:"));
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "growx");
panel.add(new JLabel("Email:"));
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "growx");
panel.add(new JButton("Submit"), "span 2, align center");
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Wonder what growx, fillx are? They will be explained in the next post
3. Column and Row Constraints
- Purpose: Define behavior for specific columns and rows.
- Examples of customization:
- Specifying fixed or variable sizes.
- Allowing columns/rows to grow, shrink, or fill available space.
- Syntax is provided in the second and third arguments of
new MigLayout().
Let’s have a look at some examples:
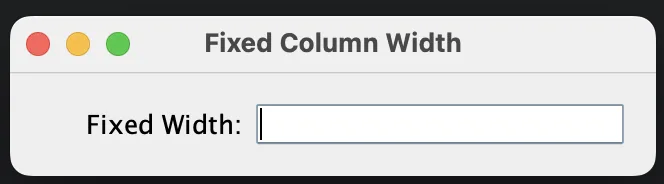
Specifying Fixed Column Width ([100px])
class FixedColumnExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Fixed Column Width");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// First column is fixed at 100px, second is default
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("", "[100px][grow]", ""));
panel.add(new JLabel("Fixed Width:"), "align right");
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "growx"); // Second column grows
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}The first column always stays 100px wide, while the second column grows if space is available.
Allowing a Column to Grow ([grow])
class GrowableColumns{
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Growable Columns");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// First column grows twice as much as the second
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("", "[grow][grow]", ""));
panel.add(new JButton("Button 1"), "growx");
panel.add(new JButton("Button 2"), "growx");
frame.add(panel);
frame.setSize(400, 100); // Set an initial size larger than needed
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}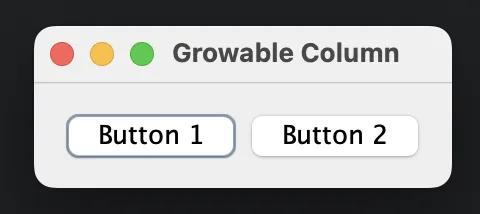
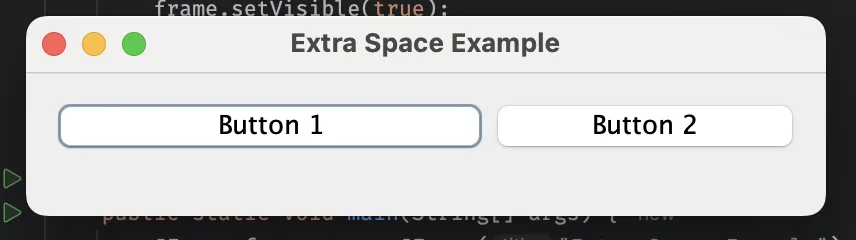
The grow option dictates how is the division of extra space is made. Consider the following example:
class GrowableColumnsUnequalGrow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Extra Space Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// First column grows twice as much as the second
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("", "[grow 2][grow 1]", ""));
panel.add(new JButton("Button 1"), "growx");
panel.add(new JButton("Button 2"), "growx");
frame.add(panel);
frame.setSize(400, 100); // Set an initial size larger than needed
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Setting Size Range ([min:pref:max])
class SizeRangeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Column Size Range");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// First column: size range 50px (min) to 200px (max), preferred is 100px
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("debug", "[50:100:200][grow]", ""));
panel.add(new JLabel("A very big column"), "align right");
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "growx");
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
The first column maintains a size between 50px and 200px but defaults to 100px if space allows.
4. Component Constraints
- Purpose: Define rules for each individual component.
- Examples of component-specific behavior:
- Spanning across multiple cells.
- Adjusting alignment within the cell.
- Controlling growth and shrinking behavior.
- Syntax is provided when adding a component (
add(component, "constraints")).
Here is an example to demonstrate components constraints:
class AlignmentCombinedExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Combined Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("debug, wrap 2", "[][grow][]", ""));
panel.add(new JLabel("Name:"), "alignx right");
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "growx");
panel.add(new JLabel("Address:"), "alignx right");
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "span 2, growx"); // Spanning 2 columns
panel.add(new JLabel("Notes:"), "alignx right");
panel.add(new JTextArea(3, 20), "span 2, growx"); // Spanning and growing
frame.add(panel);
frame.setSize(500, 200); // Set an initial size larger than preferred
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}In this example, all labels are aligned right so you can see that they are closer to the text boxes.
Also, the first textbox doesn’t have a span 2 so I just span 1 column.
Since the layout wraps at 2nd column, the 3rd column is quite insignificant. However, you can still see the first textbox is a bit shorter than the second and the third.
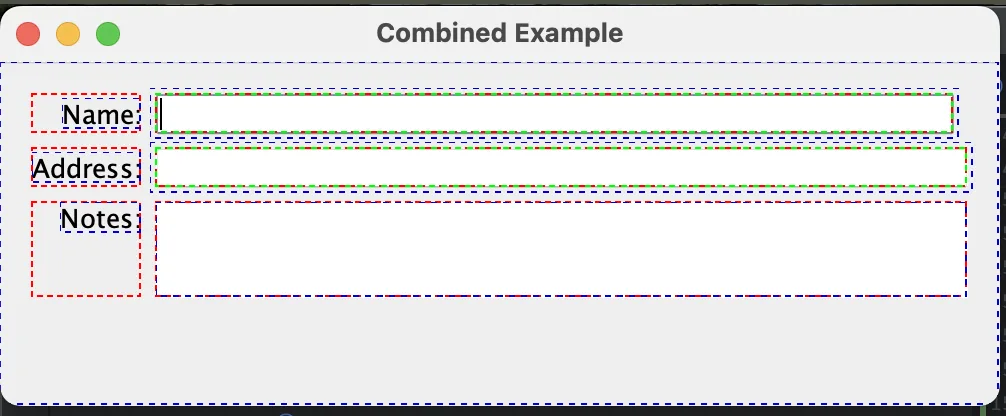
5. Dynamic Growth and Shrink
- MiGLayout can dynamically resize components to make the best use of available space.
- Components, columns, and rows can be marked as:
- Growable: Expands to take up extra space (
grow). - Shrinkable: Shrinks to fit when space is limited (
shrink).
- Growable: Expands to take up extra space (
Examples:
- Adding
growxorgrowyto a component makes it expand in that direction. - Adding
[grow]to a column allows it to expand.
Component Growth with growx
class ComponentGrowthExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Component Growth Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Layout with two columns
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("wrap 2", "[][grow]", ""));
panel.add(new JLabel("Name:"));
panel.add(new JTextField(15), "growx"); // TextField grows horizontally
frame.add(panel);
frame.setSize(400, 100); // Initial size to see growth
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}The text box component resize with the window as I resize it:
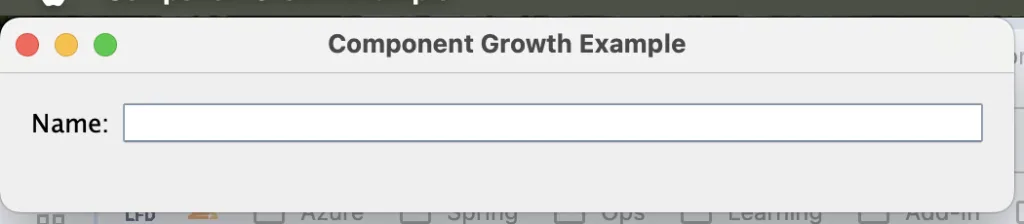
The JTextField grows horizontally when you resize the window, taking up available space in its column.
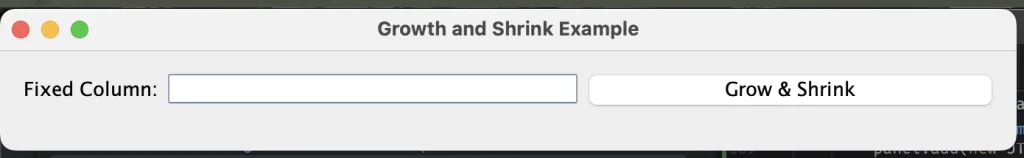
Growth and Shrink
class GrowthAndShrinkExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Growth and Shrink Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Layout with three columns: first fixed, second and third grow/shrink
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("wrap 3", "[][grow, shrink 50][grow, shrink 30]", ""));
panel.add(new JLabel("Fixed Column:"));
panel.add(new JTextField(10), "growx"); // Grows and shrinks with the column
panel.add(new JButton("Grow & Shrink"), "growx"); // Grows and shrinks with the column
frame.add(panel);
frame.setSize(600, 100); // Initial size to observe behavior
frame.setVisible(true);
}
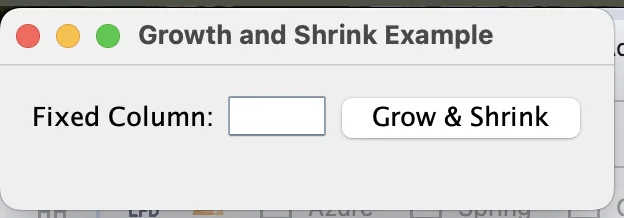
}Shrink provides finer control over how components or columns shrink, useful in more complex layouts. In the example above, shrink comes with a number signifying the aggressiveness of the shrink. The higher the number, the more possible that the component will shrink:
6. Wrapping and Gaps
- MiGLayout automatically handles wrapping and spacing between components:
- Wrapping:
- Global:
wrap nin layout constraints wraps afterncomponents. - Local:
wrapin a component’s constraints forces wrapping after that component.
- Global:
- Gaps:
- Global:
gap x ydefines default gaps between components. - Local:
gap x1 x2defines custom gaps around a specific component.
- Global:
- Wrapping:
Wrapping Components Globally (wrap n)
The wrap n layout constraint wraps to a new row after n components. java Copy code
class GlobalWrapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Global Wrap Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Wrap after 3 components
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("wrap 3"));
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
panel.add(new JButton("Button " + i));
}
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

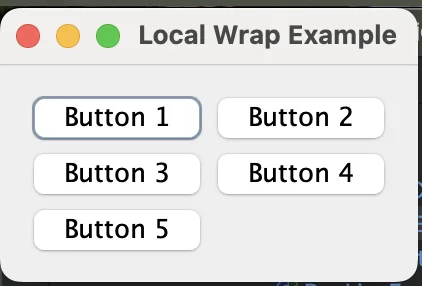
Forcing Wrapping Locally (wrap)
You can force wrapping after a specific component using the wrap constraint. java Copy code
class LocalWrapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Local Wrap Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout());
panel.add(new JButton("Button 1"));
panel.add(new JButton("Button 2"), "wrap"); // Force wrapping after this button
panel.add(new JButton("Button 3"));
panel.add(new JButton("Button 4"), "wrap"); // Force wrapping again
panel.add(new JButton("Button 5"));
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Global Gaps (gap x y)
Global gaps set default horizontal (x) and vertical (y) spacing between components. java Copy code
class GlobalGapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Global Gap Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Set global gaps: 10px horizontal, 15px vertical
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("gap 10 15"));
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
panel.add(new JButton("Button " + i));
}
frame.add(panel);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Increasing the x gap JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("gap 90 15"));

7. Debugging
- The
debugconstraint is invaluable for understanding how the grid is structured. - When enabled, it draws outlines around all cells and components, helping you visualize their positioning and size.
8. Intuitive Sizing
- MiGLayout intelligently sizes components based on:
- Their preferred size (defined by the component).
- Available space in the container.
- Constraints like
min,pref, ormaxsizes.
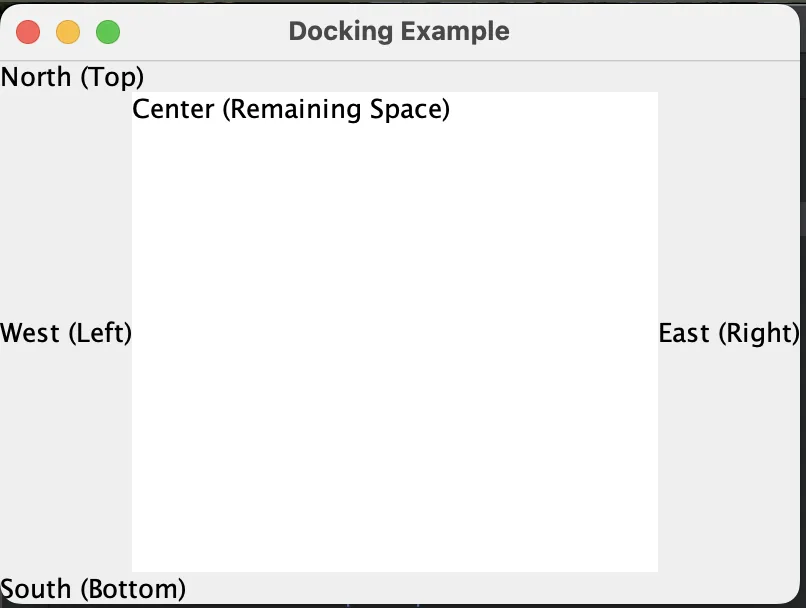
9. Docking
- Components can be docked to specific edges of the container using
dock north/south/east/west.
class DockingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Docking Example");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// MigLayout with no column or row constraints (handled by dock)
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new MigLayout("fill")); // "fill" ensures the container uses all space
// Dock components to the edges
panel.add(new JLabel("North (Top)"), "dock north");
panel.add(new JLabel("South (Bottom)"), "dock south");
panel.add(new JLabel("West (Left)"), "dock west");
panel.add(new JLabel("East (Right)"), "dock east");
// Add a central component
panel.add(new JTextArea("Center (Remaining Space)"), "dock center");
frame.add(panel);
frame.setSize(400, 300); // Set a size to observe docking
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

I build softwares that solve problems. I also love writing/documenting things I learn/want to learn.

MigLayout in 2025 :), rare gem, it’ so much easier do ui with Mig than javafx css, like a dozen ton easier.
Exactly, javafx is a mess