Table of Contents
Overview
The Set interface in java is a part of the collection framework.
Here is the overview of the classes and interfaces in this interface:
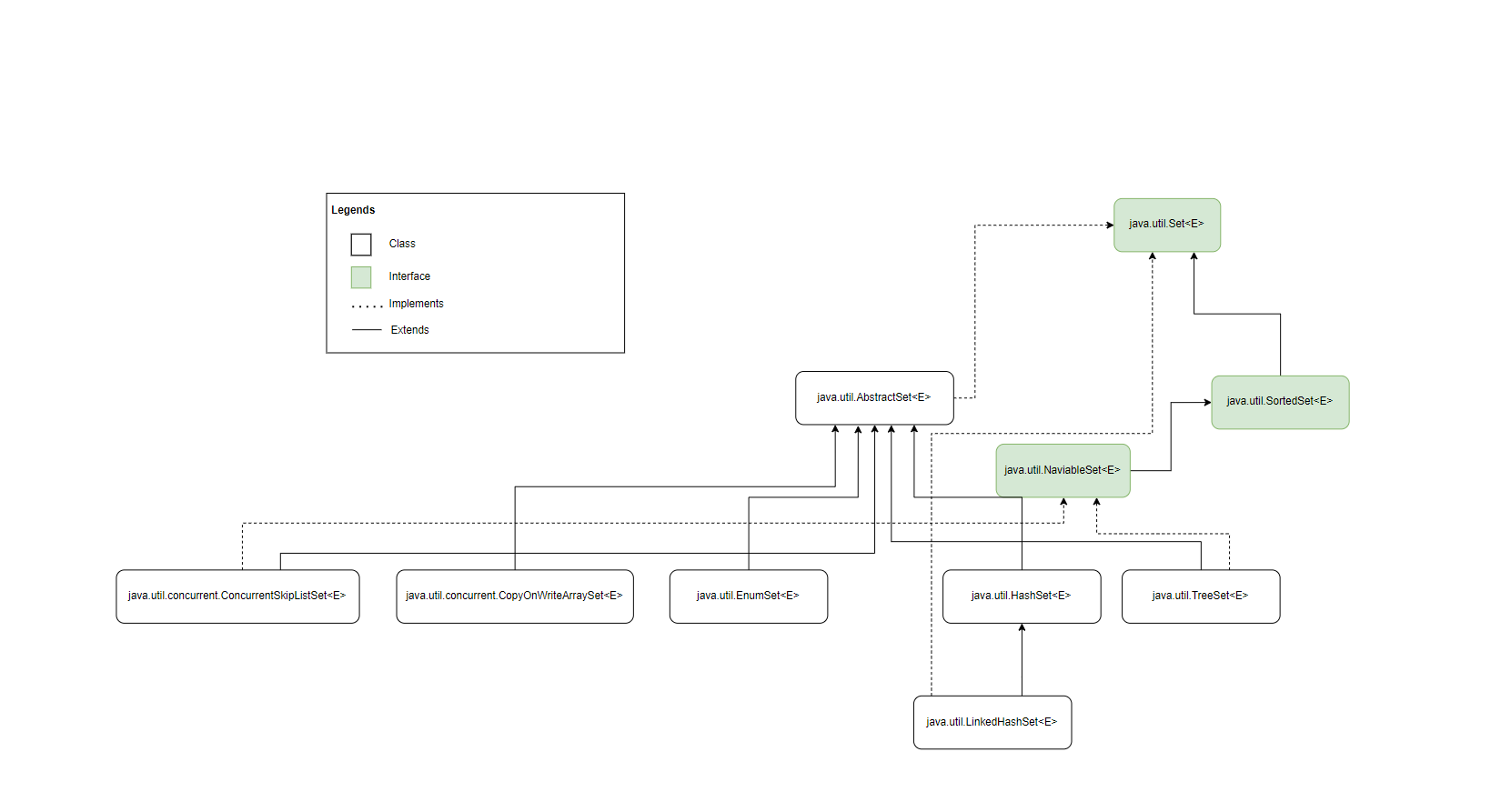
Here are some characteristics of a set:
- You cannot store duplicate values in a set
- As a result of characteristic #1, at most 1 null value is allowed (some implementations of the Set interface in java don’t allow adding null value)
Creating a set
Java, especially since version 8, provides many convenient ways to create a set. Let’s consider some of them here:
private static void createSets() {
//Create an empty set
Set<String> name = Set.of();
//Create a set with some values
Set<String> classmate = Set.of("Jane", "Jake");
//Create a set with just one element
Set<Integer> houseNumber = Collections.singleton(111);
//Create a HashSet
Set<String> friends = new HashSet<>();
friends.add("Jim");
friends.add("Kim");
}Basic Set operation
Here we explore the basic operations you can do on a Set in Java
Add elements
Set<String> mySet = new HashSet<>();
//add one element
mySet.add("Lisa");
//add many elements
mySet.addAll(List.of("Leo", "Neo", "Jake"));
Remove elements
//Remove one element
mySet.remove("Lisa");
//Remove multiple elements
mySet.removeAll(List.of("Leo", "Neo"));
//empty the set
mySet.clear();
//Use retainAll to keep only the selected elements
mySet.addAll(List.of("Jim", "Derek", "Cat", "Horseman"));
mySet.retainAll(List.of("Derek", "Cat"));
System.out.println("Now the set is: " + mySet);The output of the following code is:
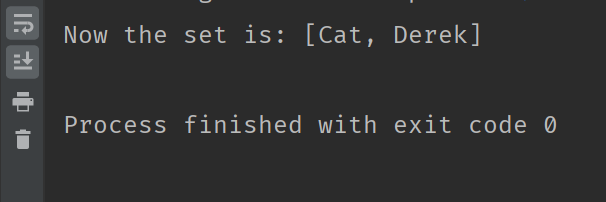
From the code above, the retainAll method removed all other elements and only kept the elements specified in the passed-in list.
Inspecting a Set
Java provides some convenient methods to inspect the status of a set:
private static void inspectSet() {
Set<String> mySet = new HashSet<>(List.of("Jake", "Luis", "Liam"));
//get number of items in the set
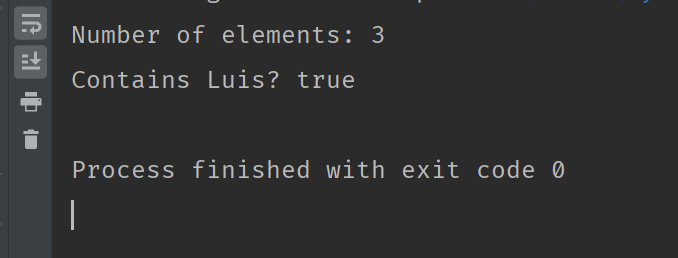
System.out.println("Number of elements: " + mySet.size());
//check if a set contain an element
System.out.println("Contains Luis? " + mySet.contains("Luis"));
}The output of that function when executed is:
Conclusion
This post provides a quick overview of the Set interface in Java. We will dig deeper in the sub interfaces and classes in other posts.

I build softwares that solve problems. I also love writing/documenting things I learn/want to learn.