Table of Contents
In this post, we’ll walk through the architecture and implementation of a simple microservices-based online store built with:
- Spring Boot 3
- RabbitMQ (asynchronous messaging)
- OpenTelemetry for distributed tracing
- Jaeger for visualizing traces
Microservices Architecture
Our online store is made up of the following services:
| Service | Responsibility |
|---|---|
catalog-service | Manages products (name, price) |
order-service | Handles orders, triggers workflow events |
inventory-service | Reserves stock when an order is placed |
payment-service | Simulates payment processing |
shipment-service | Simulates shipment creation |
All services are loosely coupled and communicate via RabbitMQ using topic exchanges.
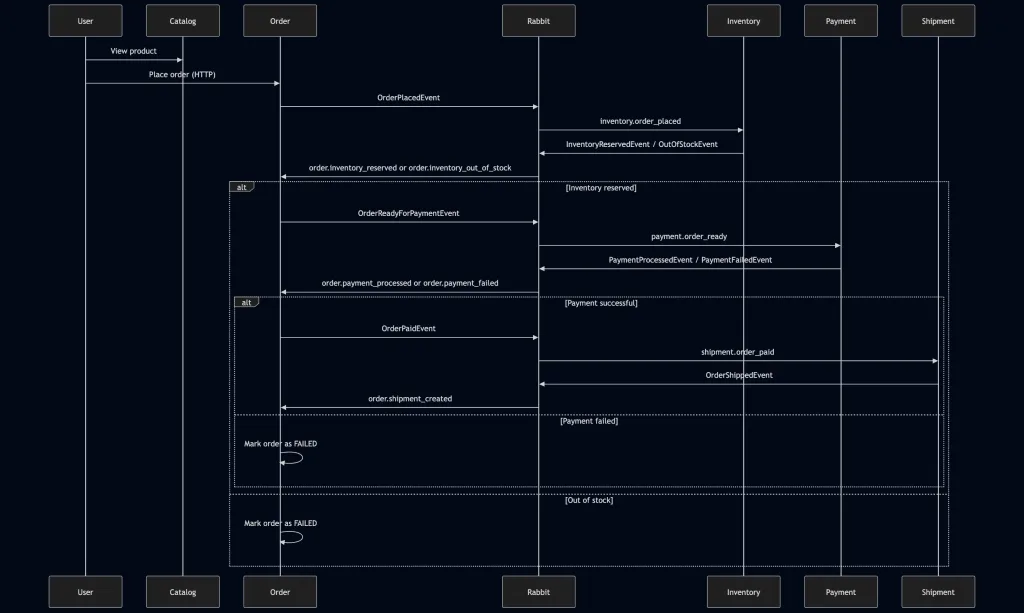
Event-Driven Flow
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Catalog
participant Order
participant Rabbit
participant Inventory
participant Payment
participant Shipment
User->>Catalog: View product
User->>Order: Place order (HTTP)
Order->>Rabbit: OrderPlacedEvent
Rabbit->>Inventory: inventory.order_placed
Inventory->>Rabbit: InventoryReservedEvent / OutOfStockEvent
Rabbit->>Order: order.inventory_reserved or order.inventory_out_of_stock
alt Inventory reserved
Order->>Rabbit: OrderReadyForPaymentEvent
Rabbit->>Payment: payment.order_ready
Payment->>Rabbit: PaymentProcessedEvent / PaymentFailedEvent
Rabbit->>Order: order.payment_processed or order.payment_failed
alt Payment successful
Order->>Rabbit: OrderPaidEvent
Rabbit->>Shipment: shipment.order_paid
Shipment->>Rabbit: OrderShippedEvent
Rabbit->>Order: order.shipment_created
else Payment failed
Order->>Order: Mark order as FAILED
end
else Out of stock
Order->>Order: Mark order as FAILED
end
Setting Up RabbitMQ
We use RabbitMQ as our message broker. In development, RabbitMQ is run as a Docker container behind the scenes.
Each service:
- Declares its own queue
- Binds to an appropriate exchange using a routing key
- Does not share queues with other services
In RabbitMQ, producers only know exchanges + routing keys.
Consumers define their own queues and bind to those routing keys.
Setting Up OpenTelemetry + Jaeger
We use OpenTelemetry to trace HTTP requests and message flow between services.
You can quickly setup jaeger with this docker compose:
services:
jaeger:
image: jaegertracing/all-in-one:1.51
ports:
- "16686:16686" # Jaeger UI
- "4317:4317" # OTLP gRPC
# Add RabbitMQ here if desiredThe agent is attached at runtime via:
-javaagent:opentelemetry-javaagent.jar \ -Dotel.service.name=order-service \ -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://YOUR_SERVER:4317 \ -Dotel.exporter.otlp.protocol=grpc
Where YOUR_SERVER is the IP address/hostname where you run the service.
You can download the java agent here:
https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-java-instrumentation/releases
Messaging Patterns
Here’s how messaging is wired:
| Event | Publisher | Consumers | Routing Key |
|---|---|---|---|
OrderPlacedEvent | order-service | inventory, payment | order.placed |
InventoryReservedEvent | inventory-service | order-service | inventory.reserved |
InventoryOutOfStockEvent | inventory-service | order-service | inventory.out-of-stock |
PaymentProcessedEvent | payment-service | order-service | payment.processed |
PaymentFailedEvent | payment-service | order-service | payment.failed |
OrderPaidEvent | order-service | shipment-service | order.paid |
OrderShippedEvent | shipment-service | order-service | shipment.created |
Domain Modeling
Each service has its own entities and data logic. Example from catalog-service:
@Entity
public class Product extends BaseEntity {
private String name;
private BigDecimal price;
}Common DTOs and events are placed in a shared common module.
Messaging Configuration Example
Each service defines its queues and bindings like this:
@Bean
public Queue orderPlacedQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("inventory.order_placed").build();
}
@Bean
public Binding bindOrderPlaced(Queue orderPlacedQueue, TopicExchange orderExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(orderPlacedQueue)
.to(orderExchange)
.with(MessagingTopics.Order.ROUTING_KEY_ORDER_PLACED);
}This binds inventory-service to the order.placed event without knowing the publisher.
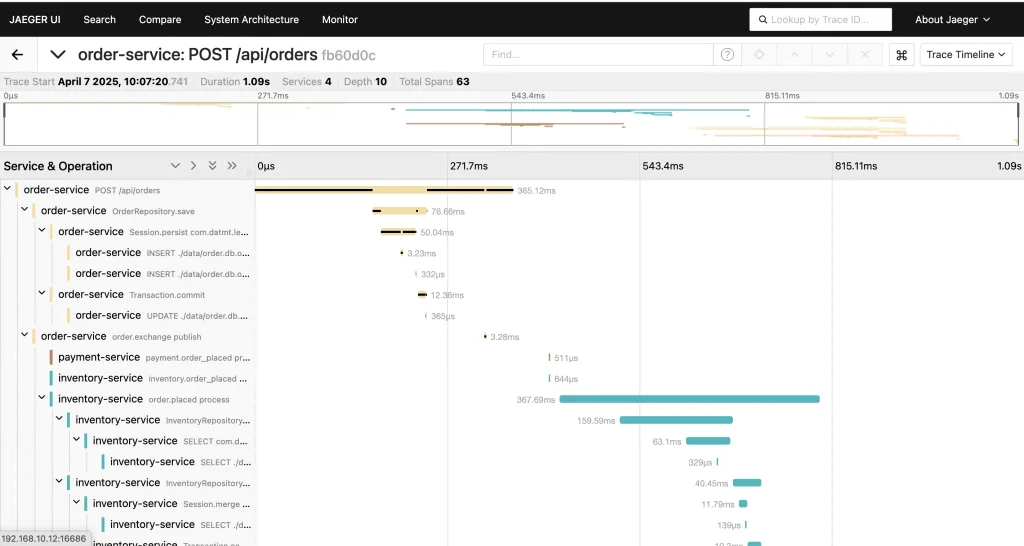
Tracing in Action
Each message span is automatically traced when using the OpenTelemetry Java agent and Jackson message converter. All spans are linked across services and visible in Jaeger.
Examples of spans:
- HTTP:
POST /orders - Messaging:
send order.placed - Messaging:
receive inventory.reserved
Summary
We’ve built a distributed system with:
- Clean microservice separation
- Asynchronous messaging via RabbitMQ
- Full distributed tracing with OpenTelemetry + Jaeger
This project demonstrates how to:
- Model a system using events and topics
- Trace cross-service operations
- Build loosely coupled, observable systems
You’re welcome to checkout the repo to run for yourself here: https://github.com/datmt/spring-microservices-rabbit-otel

I build softwares that solve problems. I also love writing/documenting things I learn/want to learn.
