Table of Contents
So recently I need to set up a quick project to store the results of my crawler in a database. Previously, I would use JDBC for this job. However, with the recent knowledge of Hibernate, why don’t I give it a go?
In this post, I’m going to show you how you can use Hibernate to store entities just like you can with frameworks like Spring but on a standalone app (commandline app/Desktop app such as JavaFX).
The application will save an entity Book into a database called book_db
Quick MariaDB setup
To quickly set up a MariaDB database, I use the following docker-compose file. I use mariadb:10.5 and PHPMyAdmin for easy access to the database. If you prefer, you can skip using PHPMyAdmin and use another version of MariaDB:
version: "3"
services:
db:
image: mariadb:10.5
container_name: db
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root
- MYSQL_DATABASE=speech_db
restart: always
ports:
- 13308:3306
volumes:
- mysql_vol:/var/lib/mysql
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
container_name: phpmyadmin
environment:
- PMA_HOST=db
- PMA_PORT=3306
restart: always
ports:
- 18811:80
volumes:
mysql_vol:Now, simply run docker-compose up -d, you have a fully functional MariaDB instance up and running.
Import Hibernates and other convenient libraries using Maven
Here is the dependency section in pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.5.7.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Other than hibernate and MySQL connector, the other are optional.
Create hibernate.cfg.xml to setup database connection
The next step would be to create a hibernate.cfg.xml file to configure the connection to the database. Where should you put this file? It should be under resources directory like I have here:
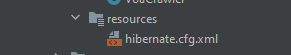
In this file, you specify the db configuration like so:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration SYSTEM
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name = "hibernate.dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
</property>
<property name = "hibernate.connection.driver_class">
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
</property>
<!-- Assume test is the database name -->
<property name = "hibernate.connection.url">
jdbc:mysql://localhost:13308/book_db
</property>
<property name = "hibernate.connection.username">
root
</property>
<property name = "hibernate.connection.password">
root
</property>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>Also, open phpMyadmin and create the following table:
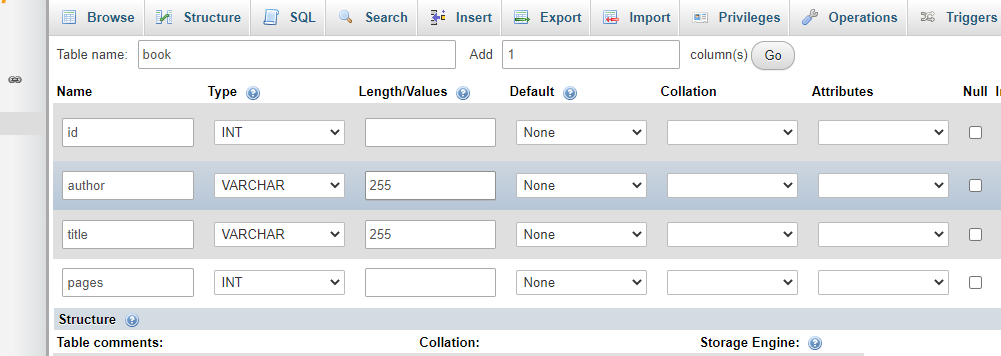
Now the hard part is done. Let’s create some entities and save them to the database.
Actually save an entity to database
Let’s create an entity like this:
package entity;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Setter
@Getter
@Table(name = "book")
public class Book {
@Id
@Column(name = "id", nullable = false)
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
String title;
String author;
int pages;
}And to save the entity, we need a session, which provided by SessionFactory. Let’s create a class that provides SessionFactory
import entity.Book;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class SessionFactoryMaker {
private static SessionFactory factory;
private static void configureFactory()
{
try {
factory = new Configuration()
.addAnnotatedClass(Book.class)
.configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println("Failed to create sessionFactory object." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static org.hibernate.SessionFactory getFactory() {
if (factory == null) {
configureFactory();
}
return factory;
}
}
One very important line in this class is #12. It is very important that you add the entity to the configuration. Without this step, hibernate will not know Book is an entity.
Finally, let’s create a book and insert it:
import entity.Book;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
public class Runner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book b = new Book();
b.setAuthor("No name");
b.setPages(2000);
b.setTitle("Some book");
SessionFactory factory = SessionFactoryMaker.getFactory();
try (Session session = factory.openSession()) {
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.save(b);
tx.commit();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Running this would create a record in the database:
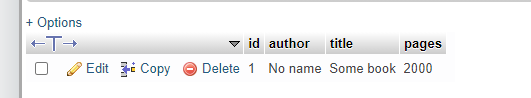
You can find the full repo here https://github.com/datmt/Hibernate-MariaDB-Standalone

I build softwares that solve problems. I also love writing/documenting things I learn/want to learn.